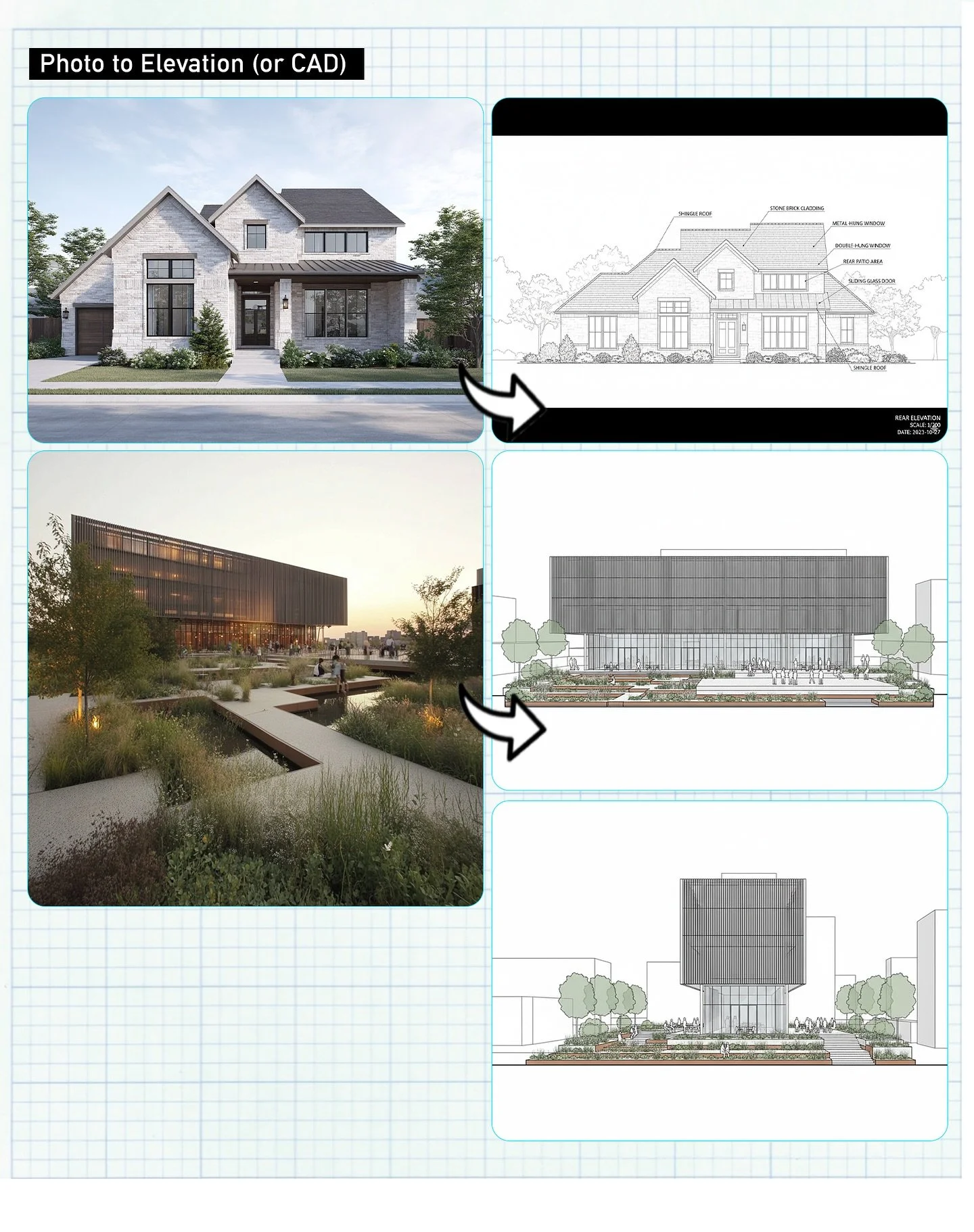
CREATIVITY
EXPERTISE
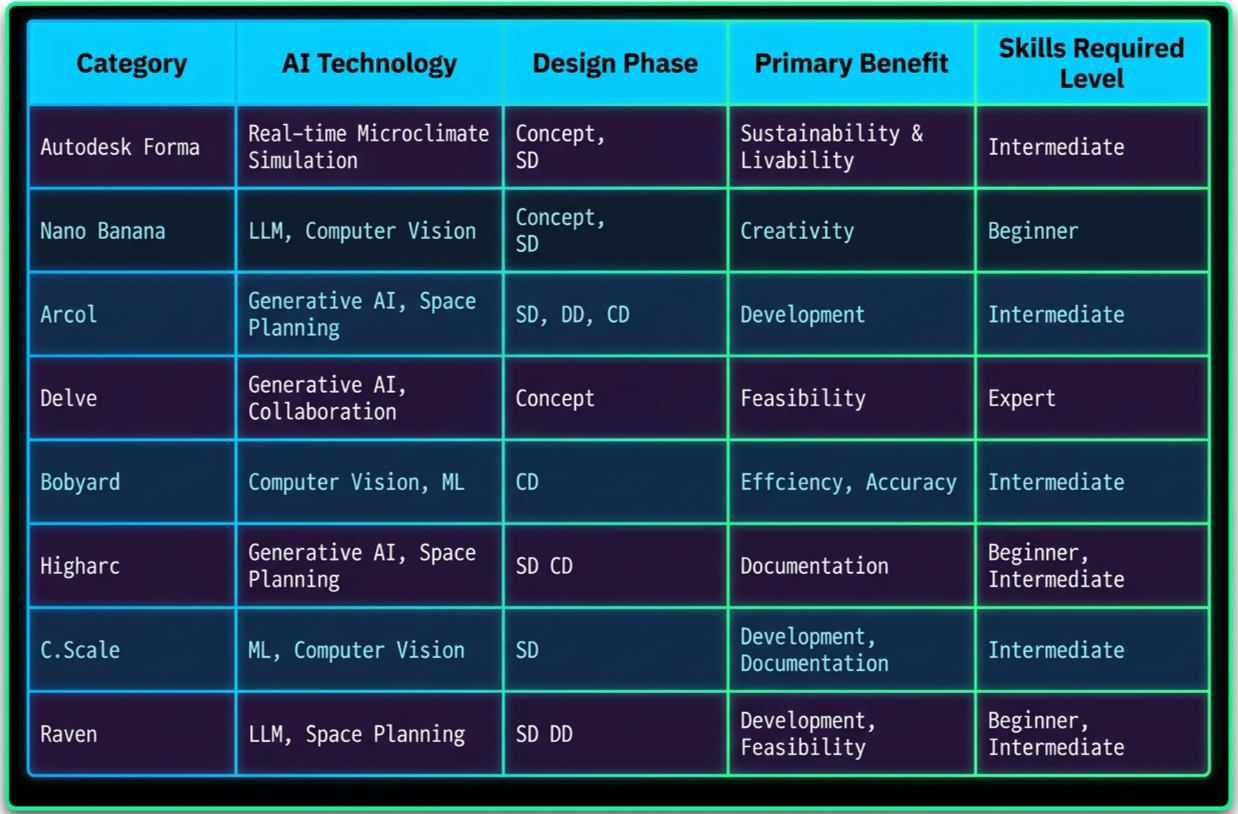
AI Tool Matrix
AI technology
·
AI Tool Matrix
·
AI technology · AI Tool Matrix ·
Part 1 :Executive Summary
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry is at a pivotal moment, transitioning from traditional desktop-based Building Information Modeling (BIM) to a cloud-native, AI-driven collaborative ecosystem.
To understand these tools, one must grasp the technological soil from which they emerged. The AEC industry has long relied on heavy, locally installed software (e.g., Revit, Rhino, AutoCAD). While powerful, these tools create significant bottlenecks in data interoperability, early-stage decision support, and cross-disciplinary collaboration.
PART 2 :Deep Tool Analysis & Classification
2.1 Autodesk Forma
-
Autodesk Forma is the core cloud offering in the Autodesk AEC Collection, designed to redefine early-stage planning. It is the successor to Spacemaker and acts as a bridge connecting concept design with detailed BIM (Revit).
-
Real-time Microclimate Simulation: Traditional wind (CFD) or solar simulations take hours. Forma uses AI-trained surrogate models to provide high-fidelity environmental analysis in seconds.
Generative Design: Users set site constraints, and algorithms generate optimal massing options.
-
Concept and Schematic Design (SD)
-
Sustainability & Livability: Ensures environmentally friendly designs via early solar, wind, noise, and carbon analysis.
Data-Driven Decisions: Translates subjective design intuition into objective performance metrics.
-
Intermediate
While the interface is intuitive, users need architectural fundamentals to interpret analysis charts (e.g., wind roses, sun hours) and understand how to adjust morphology based on data.
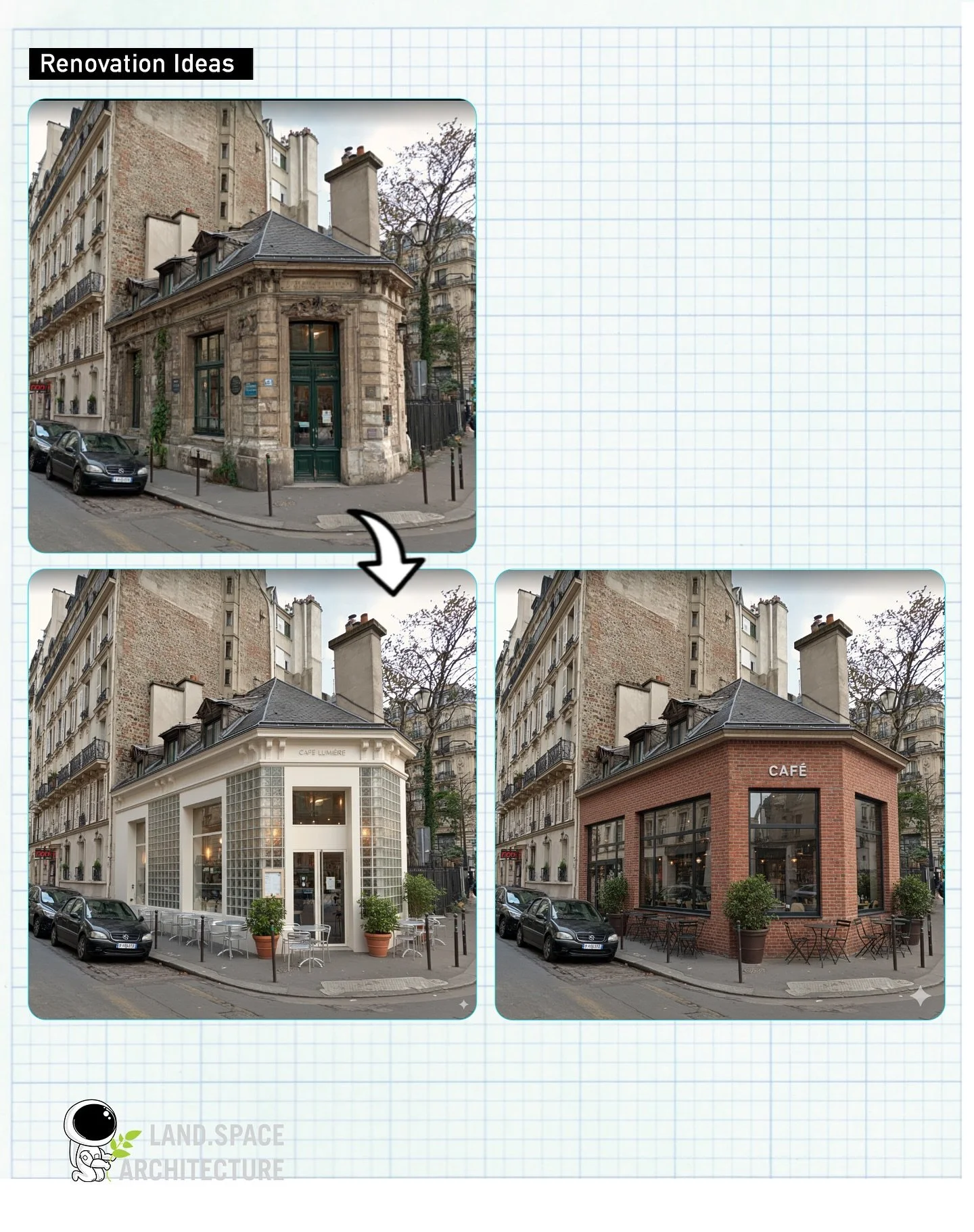
2.2 Nano Banana
-
Nano Banana" refers to the application of Google's Gemini models (Gemini 2.5 Flash / Gemini 3 Pro Image) in architecture. It represents a shift from traditional rendering to AI generative workflows, showcasing deep understanding of 3D space and blueprints.
-
Multimodal LLM: Processes both text instructions and visual inputs simultaneously.
Visual Reasoning: Unlike pixel-only generation, it understands 3D structural relationships, capable of inferring side or isometric views from a single photo.
-
Concept and Schematic Design (SD)
-
Creativity & Speed: Designers can test dozens of styles or material options in seconds via text, accelerating creative exploration.
Lower Barrier to Visualization: Enables high-quality output for those not proficient in complex rendering software.
-
Beginner
Interaction is primarily through natural language prompting. While "prompt engineering" is a skill, the technical barrier is very low.
2.3 Arcol
-
Often dubbed the "Figma for Building Design," Arcol is a fully browser-based BIM tool. It breaks down collaboration barriers inherent in desktop software, aiming to take over design phases with a smoother UX
-
Parametric Geometry Engine: Currently relies on deterministic modeling (booleans, lofts) but has a roadmap for Text-to-Geometry generative AI.
Automated Compliance: Built-in algorithms calculate Floor Area Ratio (FAR), setbacks, and parking counts in real-time.
-
Schematic Design (SD) and Design Development(DD)
-
Real-time Collaboration: Supports "Multiplayer" mode where multiple users work in the same model simultaneously, solving version control issues.
Accessibility: Web-based access allows non-pros (clients, developers) to view and comment without installing heavy software.
-
Intermediate
While the UI is cleaner than Revit, users still need to understand core BIM concepts (components, constraints, layers) and construction logic.
2.4 Delve
-
Originally developed by Sidewalk Labs, Delve is a generative design tool for urban master planning. It tightly couples physical design with financial modeling to find "optimal solutions".
-
Generative Design: Uses machine learning to generate hundreds of planning layouts based on constraints (sunlight, density, budget).
Multi-Objective Optimization: Algorithms balance conflicting goals (e.g., maximizing sellable area vs. public green space) and rank options.
-
Concept
-
Feasibility & Value: Uncovers high-value design options that human designers might miss.
Risk Quantification: Quantifies the impact of design decisions on cost and revenue via massive scenario analysis
-
Expert
Users need knowledge of urban planning, real estate finance, and optimization logic to correctly set parameters and interpret results.
2.5 Bobyard
-
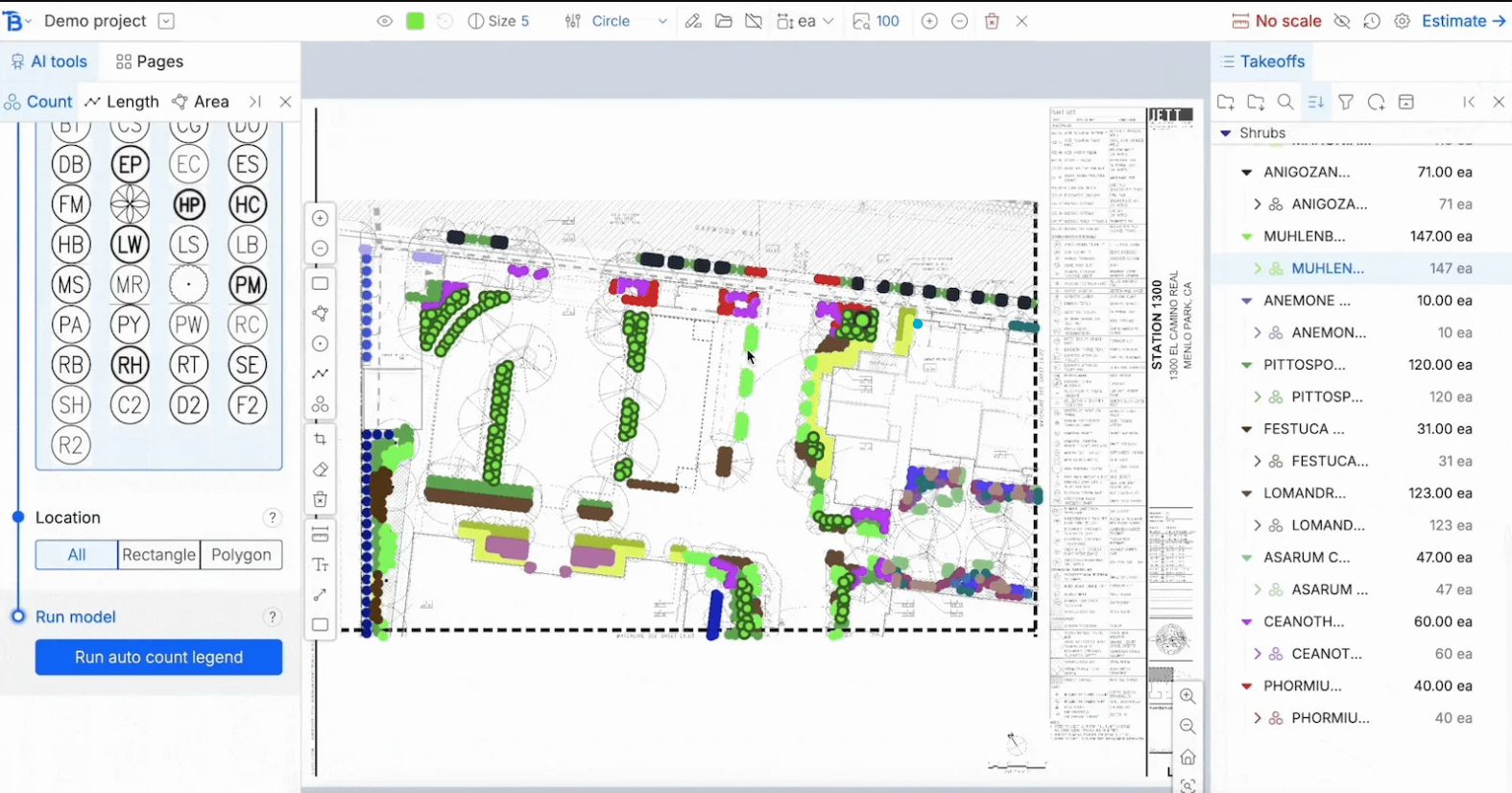
Bobyard is a vertical AI tool for the landscape industry, automating pre-construction "takeoffs" and estimation. It uses computer vision to handle tedious counting and measuring tasks.
-
Computer Vision: Identifies specific symbols (trees, shrubs) and areas in PDF drawings.
Pattern Recognition: Trained on messy landscape drawings, it distinguishes overlapping lines and non-standard symbols.
Machine Learning: Adapts to different drafting styles to improve accuracy over time
-
CD
-
Efficiency & Speed: Users report 10x faster takeoffs, reducing days of work to hours.
Accuracy: Reduces human error in counting, leading to more competitive bids.
-
Intermediate
While identification is automated, users must have professional estimating knowledge to verify results and apply correct pricing/construction logic.
2.6 Higharc
-
Higharc is an all-in-one web platform for production homebuilders. By defining homes as data rather than static drawings, it automates the flow from design to sales and construction.
-
Generative AI (AutoLayout): Automatically generates intelligent 3D models from sketches or PDFs, populating rooms with components.
Rule-Based Engine: Relies on strict parametric rules to ensure generated drawings meet building codes and constructability standards.
-
SD & CD
-
Documentation Automation: Automatically generates lot-specific construction drawings without manual redrawing.
Sales Integration: Design changes are instantly reflected in sales materials, removing information gaps
-
Beginner & Intermediate
The tool makes drafting accessible to non-experts (e.g., sales staff), though setting up the system requires expert knowledge. As a user tool, it lowers the barrier significantly.
2.7 C.Scale
-
Spun out of EHDD Architecture, C.Scale is a dedicated engine for Whole Life Carbon (WLC) analysis, addressing the lack of carbon data in early design.
-
Machine Learning Prediction: Trained on global datasets, it predicts a project's carbon footprint based on minimal inputs (massing, location, usage).
Data Augmentation: Fills data gaps with regional background data and climate projections
-
Concept & SD
-
Decarbonization: Identifies high-impact reduction strategies (structure, energy systems) when they matter most.
Benchmarking: Compares current designs against industry standards or portfolios
-
Intermediate
The tool is easy to access (no login required for some features), but interpreting results requires sustainability/LCA knowledge.
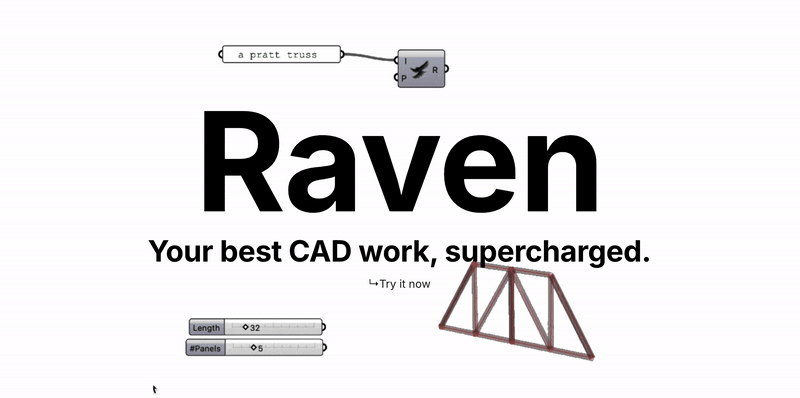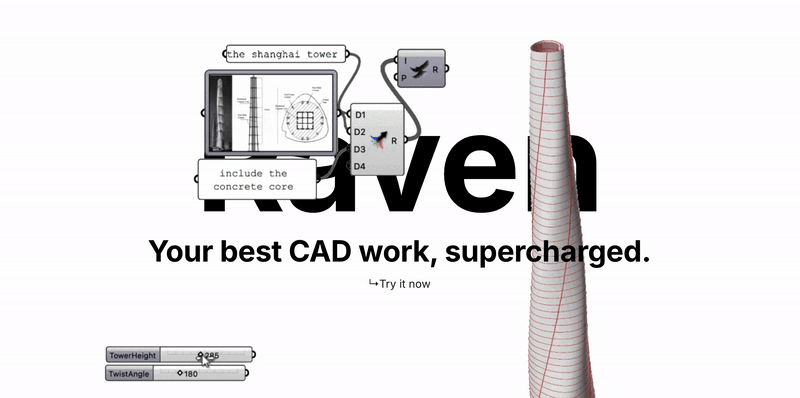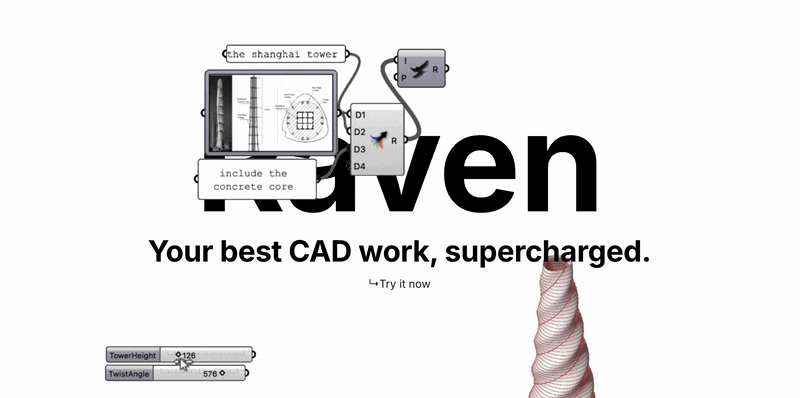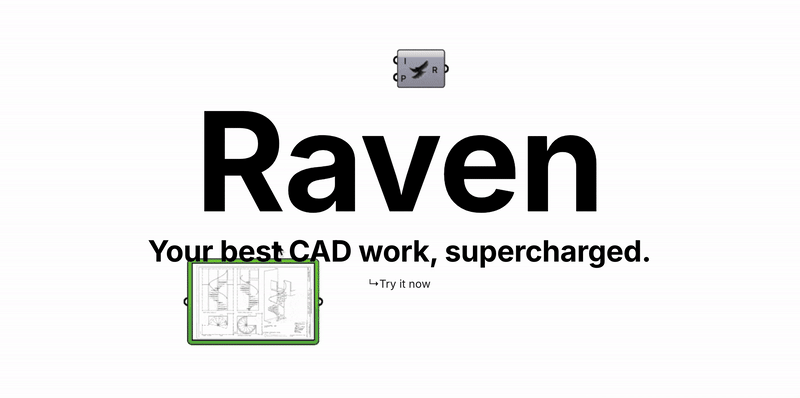
2.8 Raven
-
Raven is an AI plugin for Rhino/Grasshopper that lowers the barrier to parametric design. It uses AI agents to write and debug complex visual scripts.
-
LLM Code Generation: Converts natural language (e.g., "create a twisting tower") into Grasshopper scripts.
Debugging & Reasoning: Understands script logic to fix errors or optimize structure.
-
SD & DD
-
Empowerment: Allows designers without programming skills to use advanced parametric tools.
Workflow Acceleration: Generates base scripts quickly, saving time for experienced users
-
Beginner & Intermediate
Raven's goal is to let Beginners perform tasks that previously required Expert skills
The eight tools analyzed demonstrate a profound shift in AEC from "Computer-Aided Drafting" to "AI-Augmented Agency."
Forma and C.Scale set new standards for performance-based planning.
Nano Banana and Raven introduce assistants that understand human intent.
Arcol and Higharc rebuild the collaboration infrastructure on the cloud.
Delve and Bobyard turn optimization and automation directly into business value.
I found the Raven promising me a lot at the parametric design. General-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) are being augmented by vertical, domain-specific models. Raven applies LLMs to Grasshopper scriptwriting and demonstrates a multimodal understanding of architectural blueprints. AI is evolving from simply "generating images" to generating logic and generating data.
Successful adoption requires not just software upgrades, but a restructuring of business workflows to leverage these new agile, data-driven capabilities.